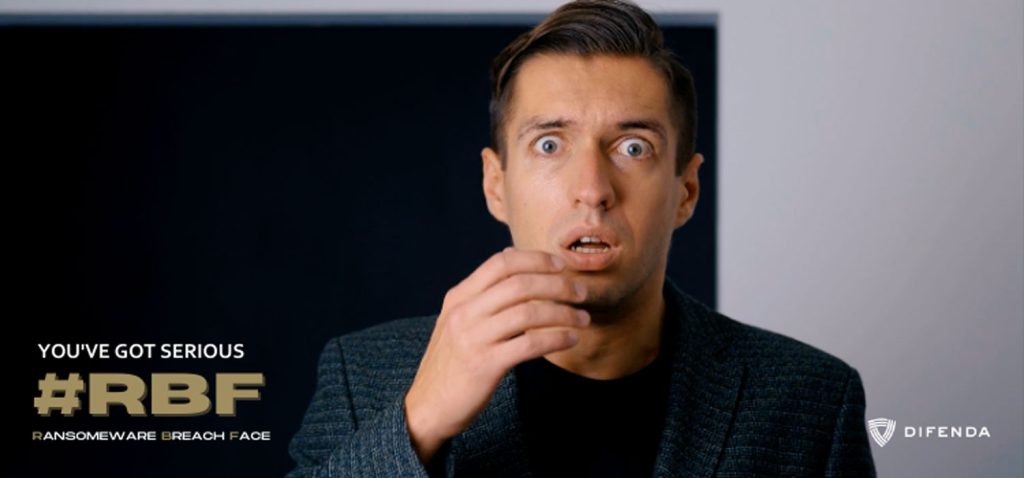
Ransomware Breach Face happens to people who unintentionally appear surprised, shocked, saddened, or frightened when they accidentally cause a cyber breach within their company.
Basically, it happens when you accidentally click on a phishing email or receive a Ransome note.
Some other, common reactions include:
- Panic: Some people may realize that they have caused a cyber breach and feel panicked about the potential consequences, such as identity theft or financial loss.
- Embarrassment: Some people may feel embarrassed or ashamed about falling for the scam, especially if they believe that others may have been affected.
- Anger: People may feel angry at themselves or the attacker for being tricked, which can lead to feelings of frustration and helplessness.
- Denial: Some people may try to deny that they have fallen for an attack and may try to rationalize their actions in order to avoid accepting responsibility.
- Resentment: Others may accept that they have fallen for a phishing scam and may feel helpless to do anything about it.
This shocked/stressed expression is what we like to call #RBF or Ransomware Breach Face.
The Anatomy of #RBF
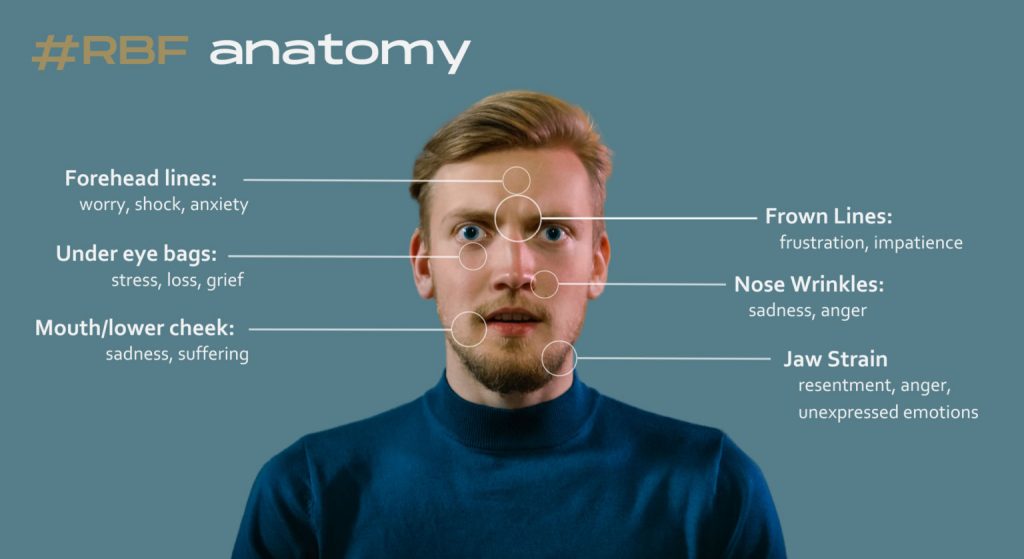
Why are ransomware breaches so prevalent in 2023?
The prevalence of Ransomware Breach Face has reached an all-time high in 2023, and people in all business sizes and industries are at risk.
The COVID-19 pandemic has resulted in a significant increase in remote work, and many organizations have struggled to secure their remote networks and endpoints, making them more vulnerable to ransomware attacks. With more employees working from home, attackers have more opportunities to exploit security gaps and breach an organization’s network.
The growth of the ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model has also made it easier for attackers with limited technical knowledge to launch ransomware attacks. RaaS providers offer turnkey solutions that include malware, hosting, and support services, making it easier for attackers to launch sophisticated attacks.
Most notably, organizations are generating and collecting more data than ever. The value of this information on the Black Market has increased, making it a lucrative endeavor for cybercriminals. Ransomware attacks allow attackers to encrypt an organization’s data and demand a ransom for the decryption key, making it an attractive option for cybercriminals seeking to make a profit.
But just because ransomware is becoming more common doesn’t mean those well-versed in the cybersecurity space should have problems avoiding these scams.
So, why is #RBF so prevalent today?
More people are falling for ransomware attacks for several reasons:
- Increased Social Engineering Techniques: Ransomware attackers are becoming more sophisticated in their use of social engineering techniques, such as phishing emails, to trick people into downloading malware or giving up sensitive information. These attacks often appear to come from a trusted source, making them difficult to detect.
- Lack of Awareness: Many people are not aware of the dangers of ransomware and the tactics used by attackers, and as a result, they may unknowingly fall for these attacks.
- Weak Security Measures: Some organizations have weak security measures in place, such as outdated antivirus software or a lack of employee training, which increases their vulnerability to ransomware attacks.
- Human Error: Despite the best security measures, human error remains one of the biggest factors in successful ransomware attacks. With the increased financial and economic pressures in 2023, human error is even higher as many employees are increasingly distracted. Employees may inadvertently open a malicious email attachment or download software from an untrusted source, putting the organization at risk.
To protect your organization from ransomware attacks, businesses need to take proactive steps to secure their networks and endpoints.
How to reduce the impact of #RBF
Regardless of your initial reaction, it is important for individuals and businesses to take steps to protect themselves from the consequences of a ransomware attack. Including reporting the phishing attempt to the appropriate authorities and changing any compromised passwords.
It is also important for individuals to educate themselves about ransomware and to be vigilant when receiving emails, texts, or phone calls from unknown sources.
3 things businesses can do to prevent a Ransomware Breach Face include:
- Employee Training: One of the most effective ways to prevent a cyber attack is to educate employees about the dangers of phishing, social engineering, and other types of cyber attacks. Regular training and awareness programs can help employees recognize and avoid these threats.
- Strong Security Measures: Implementing strong security measures such as firewalls, antivirus software, and encryption can help prevent cyber attacks by reducing the vulnerability of the network and sensitive information.
- Incident Response Plan: Developing and regularly testing an incident response plan can help a business respond quickly and effectively to a cyber attack. The plan should include procedures for identifying and containing the attack, restoring systems and data, and reporting the incident to the appropriate authorities.


